Merge Sort Algorithm
Merge Sort Algorithm
Merge Sort is a kind of Divide and Conquer algorithm in computer programrming. It is one of the most popular sorting algorithms and a great way to develop confidence in building recursive algorithms.
Divide and Conquer Strategy
Using the Divide and Conquer technique, we divide a problem into subproblems. When the solution to each subproblem is ready, we 'combine' the results from the subproblems to solve the main problem.
Suppose we had to sort an array A. A subproblem would be to sort a sub-section of this array starting at index p and ending at index r, denoted as A[p..r].
Divide
If q is the half-way point between p and r, then we can split the subarray A[p..r] into two arrays A[p..q] and A[q+1, r].
Conquer
In the conquer step, we try to sort both the subarrays A[p..q] and A[q+1, r]. If we haven't yet reached the base case, we again divide both these subarrays and try to sort them.
Combine
When the conquer step reaches the base step and we get two sorted subarrays A[p..q] and A[q+1, r] for array A[p..r], we combine the results by creating a sorted array A[p..r] from two sorted subarrays A[p..q] and A[q+1, r]
The MergeSort Algorithm
The MergeSort function repeatedly divides the array into two halves until we reach a stage where we try to perform MergeSort on a subarray of size 1 i.e. p == r.
After that, the merge function comes into play and combines the sorted arrays into larger arrays until the whole array is merged.
MergeSort(A, p, r)If p > rreturn;q = (p+r)/2;mergeSort(A, p, q)mergeSort(A, q+1, r)merge(A, p, q, r)
To sort an entire array, we need to call MergeSort(A, 0, length(A)-1).
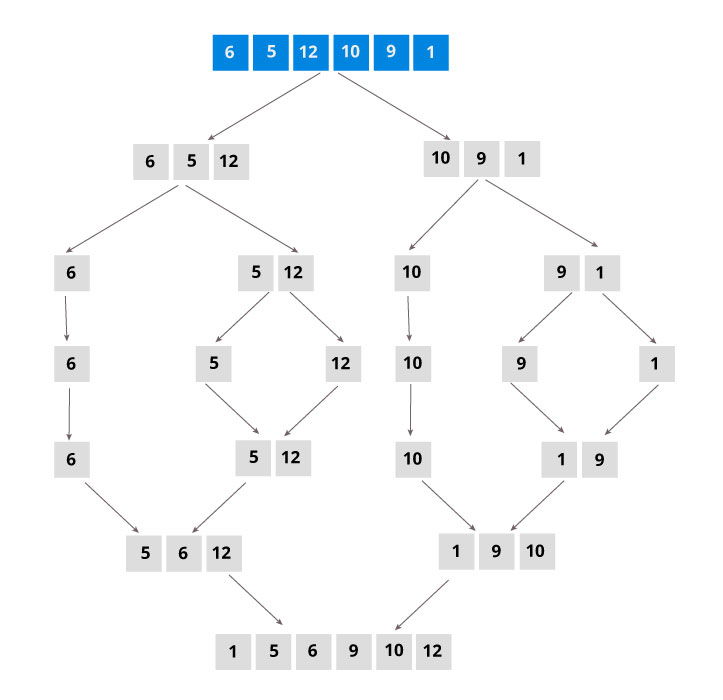
As shown in the image below, the merge sort algorithm recursively divides the array into halves until we reach the base case of array with 1 element. After that, the merge function picks up the sorted sub-arrays and merges them to gradually sort the entire array.

The merge step of merge sort
Every recursive algorithm is dependent on a base case and the ability to combine the results from base cases. Merge sort is no different. The most important part of the merge sort algorithm is, you guessed it, the "merge" step.
The merge step is the solution to the simple problem of merging two sorted lists(arrays) to build one large sorted list(array).
The algorithm maintains three pointers, one for each of the two arrays and one for maintaining the current index of final sorted array.
Have we reached the end of any of the arrays?
No:
Compare current elements of both arrays
Copy smaller element into sorted array
Move pointer of element containing smaller element
Yes:
Copy all remaining elements of non-empty array

Writing the code for merge algorithm
A noticeable difference between the merging step we described above and the one we use for merge sort is that we only perform the merge function on consecutive sub-arrays.
This is why we only need the array, the first position, the last index of the first subarray(we can calculate the first index of second subarray) and the last index of second subarray.
Our task is to merge two subarrays A[p..q] and A[q+1..r] to create a sorted array A[p..r]. So the inputs to the function are A, p, q and r
The merge function works as follows:
- Create copies of the subarrays L ← A[p..q] and M ← A[q+1..r].
- Create three pointers i,j and k
- i maintains current index of L, starting at 1
- j maintains current index of M, starting at 1
- k maintains current index of A[p..q], starting at p
- Until we reach the end of either L or M, pick the larger among the elements from L and M and place them in the correct position at A[p..q]
- When we run out of elements in either L or M, pick up the remaining elements and put in A[p..q]
In code, this would look like:
void merge(int A[], int p, int q, int r){/* Create L ← A[p..q] and M ← A[q+1..r] */int n1 = q - p + 1;int n2 = r - q;int L[n1], M[n2];for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)L[i] = A[p + i];for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)M[j] = A[q + 1 + j];/* Maintain current index of sub-arrays and main array */int i, j, k;i = 0;j = 0;k = p;/* Until we reach either end of either L or M, pick larger among elements L and M and place them in the correct position at A[p..r] */while (i < n1 && j < n2){if (L[i] <= M[j]){arr[k] = L[i];i++;}else{arr[k] = M[j];j++;}k++;}/* When we run out of elements in either L or M, pick up the remaining elements and put in A[p..r] */while (i < n1){A[k] = L[i];i++;k++;}while (j < n2){A[k] = M[j];j++;k++;}}
Merge function explained step-by-step
There is a lot happening in this function, so let's take an example to see how this would work.
As usual, a picture speaks a thousand words.

The array A[0..8] contains two sorted subarrays A[1..5] and A[6..7]. Let us see how merge function will merge the two arrays.
void merge(int A[], int p = 1, int q = 4, int 6){
Step 1: Create duplicate copies of sub-arrays to be sorted
/* Create L ← A[p..q] and M ← A[q+1..r] */n1 = 4 - 1 + 1 = 4;n2 = 6 - 4 = 2;int L[4], M[2];for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)L[i] = A[p + i];/* L[0,1,2,3] = A[1,2,3,4] = [1,5,10,12] */for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)M[j] = A[q + 1 + j];/* M[0,1,2,3] = A[5,6] = [6,9]

Step 2: Maintain current index of sub-arrays and main array
int i, j, k;i = 0;j = 0;k = p;

Step 3: Until we reach end of either L or M, pick larger among elements L and M and place them in the correct position at A[p..r]
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {if (L[i] <= M[j]) {A[k] = L[i]; i++;}else {A[k] = M[j];j++;}k++;}

Step 4: When we run out of elements in either L or M, pick up the remaining elements and put in A[p..r]
/* We exited the earlier loop because j < n2 doesn't hold */while (i < n1){A[k] = L[i];i++;k++;}

/* We exited the earlier loop because i < n1 doesn't hold */while (j < n2){A[k] = M[j];j++;k++;}}

This step would have been needed if size of M was greater than L.
At the end of the merge function, the subarray A[p..r] is sorted.
Comments
Post a Comment